Anemia is a condition in which the number of red blood cells or their oxygen-carrying capacity is insufficient to meet the body’s physiological requirements, which vary by age, sex, altitude, smoking habits, and during pregnancy.
Here are some problems related to anemia:
1. Problem:
A poor anemic woman of gravida 3, and in the 3rd trimester of pregnancy has attended PHC for the 1st time. Her Hb% is 7.5 gm/dl, weight is 50 kg. How will you manage?
1.Solution:
As we can see from the case history, the risk factors we can recognize are:
- Moderate anemia
- Poverty, lack of nutrition
- Multigravida
- Lack of health-seeking behavior
- Not taken antenatal care
Investigations for the cause of anemia:
- History
- Cause of blood loss if any
- Diet practices
- Lab investigations: Complete hemogram(CBC & ESR), Stool examination for hookworms & occult blood, Iron saturation (TIBC), Serum ferritin levels.
Management:
- A pregnant mother should have a minimum of 11 gm/dl of hemoglobin.
- Here, the woman is having only 7.5 gm/dl of hemoglobin.
- Hence, anemia should be corrected immediately by parental iron therapy.
Treatment plan for moderate anemia in pregnancy:
Calculation of Iron requirement in mg:
= (Normal Hb%➖ Patient's Hb%) ✖ Weight in kg ✖ 2.21➕ 1000
= (11-7.5) ✖ 50 ✖ 2.21 ➕ 1000
= 3.5 ✖ 50 ✖ 2.21➕ 1000
= 386.75 ➕ 1000
= 1386.75 (to round up to 1400 mg)
Hence, iron requirement is 1400 mg.
Inferon (100 mg) is given IM daily for 15 days.
Oral treatment is continued for 3 months after Hb% has returned to normal.
Assessment of hemoglobin periodically.
Preventive measures:
The woman is advised to
- Take more iron rich foods: Green leafy vegetables, jaggery, etc.
- Attend supplementary nutrition programmes at Anganwadi (ICDS).
- Take antenatal care (ANC).
- Take Albendazole 400 mg.
- Health education regarding anemia & it's complications.
- Improvement of socioeconomic problems.
- Plan for institutional delivery.
- Plan for undergoing tubectomy.
2. Problem:
What are the anatomic sites to be examined for detecting pallor?
2. Solution:
- Lower palpebral conjunctiva
- Tongue and oral mucosa
- Nails
- Palms of hands
3. Problem:
What are the advices to be given to a recipient taking the IFA tablet?
3. Solution:
- The IFA tablet should be consumed after meals to avoid gastric discomfort and nausea.
- Black stools may be passed after consuming IFA tablets.
- One can experience loose stools or constipation for some time but this will settle after some days.
- Do not take the tablets with tea, coffee or milk as these may interfere with absorption of iron.
- Do not take Calcium tablets at the same time as calcium inhibits absorption of iron.
- Pregnant or lactating women must consume the tablets daily.
4. Problem:
What are the contraindications for IFA prophylaxis?
4. Solution:
Prophylaxis with iron should not be given in case of
- Acute illness (fever, acute diarrhea, pneumonia, etc.)
- Severe acute malnutrition (SAM)
- Known case of hemoglobinopathy
- History of repeated blood transfusion.
5. Problem:
What are the measures to prevent anaemia in children?
5. Solution:
Besides the supplementation, the following measures should be taken simultaneously as long-term measures to prevent IDA in children:
- Exclusive breastfeeding promotion for the first 6 months of life.
- Adequate & appropriate complementary feeding with iron-rich foods till 2 years of age.
- Different variety of foods rich in absorbable vitamins and minerals to be included.
- To increase the bioavailability of iron in usual diets altering the meal patterns.
- Diagnosis, treatment & prevention of parasitic infections.
- Screening of target groups for moderate/severe anaemia and referring these cases to an appropriate health facility.
6. Problem:
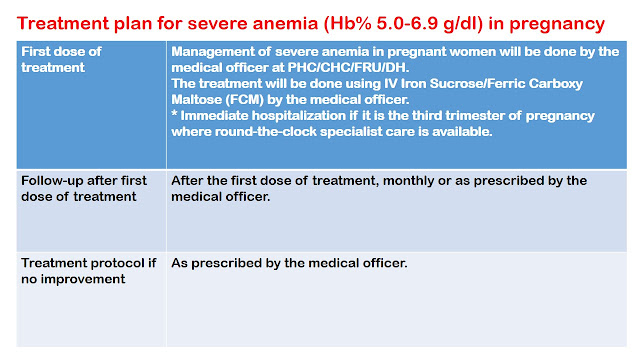
How will you manage mild & severe anemia in pregnancy at PHC?
6. Solution:
7. Problem:
What are the doses of IFA for different age groups for prophylaxis of anemia?
7. Solution:
8. Problem:
What are the doses of Albendazole for different age groups for deworming?
8. Solution:
9. Problem:
What are the foods which enhance the absorption of iron & inhibit iron absorption?
9. Solution:
Enhancers of the iron absorption:
1. Haem iron: present in meat, poultry, fish, and seafood.
2. Ascorbic acid or vitamin C: present in fruits, juice, potatoes and some other tubers and other vegetables such as green leaves, cauliflower, and cabbage.
3. Fermented or germinated food.
2. Ascorbic acid or vitamin C: present in fruits, juice, potatoes and some other tubers and other vegetables such as green leaves, cauliflower, and cabbage.
3. Fermented or germinated food.
Inhibitors of iron absorption:
1. Cereal bran, cereal grains, high-extraction flour, legumes, nuts, and seeds.
2. Tea, coffee, cocoa, herbal infusions in general, certain spices (e.g. oregano).
3. Calcium, particularly from milk and milk products.
1. Cereal bran, cereal grains, high-extraction flour, legumes, nuts, and seeds.
2. Tea, coffee, cocoa, herbal infusions in general, certain spices (e.g. oregano).
3. Calcium, particularly from milk and milk products.










No comments:
Post a Comment